إن تقرير تحقيقات فيرايزون 2024 لاختراق البيانات لعام 2024 وجدت أن 80% من الاختراقات تحدث بسبب بيانات الاعتماد المسروقة. لهذا السبب 61% من المؤسسات تتطلع إلى التحول إلى العمل بدون كلمة مرور في عام 2025.
على الرغم من سوء كلمات المرور المسروقة - وهي سيئة حقاً - إلا أنها ليست المشكلة الوحيدة. لقد قام مجرمو الإنترنت بتصنيع الهجمات:
- ارتفعت البرمجيات الخبيثة كخدمة (MaaS) بنسبة 4,0001 تيرابايت إلى 4,0001 تيرابايت، لكل آوتسير, ، والتي وجدت أيضًا أن حركة المرور على الخدمات المصرفية عبر الهاتف المحمول تمثل الآن 85% من المعاملات المصرفية الرقمية، مما يجعل الخدمات المالية هدفًا رئيسيًا.
- تتصاعد تهديدات الهوية القائمة على الذكاء الاصطناعي. في اليابان, فإن المهاجمين يستخدمون عمليات التزييف العميق والهندسة الاجتماعية لانتحال شخصية متحدثي اللغة اليابانية بطلاقة وخداع مكاتب المساعدة لإعادة تعيين بيانات الاعتماد.
- تقدم مجموعة أدوات التصيّد الاحتيالي Darcula أسلوبًا جديدًا للتصيد الاحتيالي كخدمة (PhaaS) يسمح لمجرمي الإنترنت "ببساطة بنسخ ولصق أي عنوان URL في الواجهة... وستقوم المنصة بإنتاج مجموعة تصيّد احتيالي كاملة"، وفقًا القراءة المظلمة.
وعلى الرغم من تزايد اعتماد المصادقة متعددة العوامل (MFA) في مختلف القطاعات، إلا أن الهجمات لا تتباطأ. وكما يقول آنت آلان من مؤسسة Gartner: "إن المصادقة متعددة العوامل (MFA) هي طريقة تفكير عفا عليها الزمن بشكل متزايد. المهم هو كيف يمكن الجمع بين بيانات الاعتماد والتعرّف والتأكيد وإشارات المخاطر لتوفير الثقة الكافية في ادعاء الهوية."
كان من المفترض أن يوقف MFA الهجمات. فما الذي يحدث؟
تُظهر الاختراقات الأخيرة أن المصادقة الآلية التقليدية وحدها لا توقف المهاجمين:
- ذكرت شركة MGM للمنتجعات $100 مليون في الأضرار بعد أن استخدم المهاجمون بيانات اعتماد Okta المسروقة من أجل التلاعب الاجتماعي في طريقهم لتجاوز MFA، مما تسبب في واحدة من أكبر حالات التعطيل الإلكتروني في تاريخ الضيافة.
- استغل المخترقون واجهات برمجة التطبيقات غير الآمنة لتجاوز ضوابط المصادقة في S. وزارة الخزانة
- عيب في مايكروسوفت Azure MFA ثغرة أمنية في تجاوز المصادقة تركت "ملايين الحسابات عرضة للدخول غير المصرح به"، وفقًا مجلة إنفوسيكيوريتي.
إذاً، ما هو الحل؟ المصادقة الحديثة.
المصادقة الحديثة بدون كلمة مرور بشكل افتراضي، ومدرك للمخاطر، وقابل للتكيف باستمرار. فهو يدمج معلومات المستخدم ومعلومات الوصول والسياق وإشارات المخاطر لمصادقة المستخدمين بشكل ديناميكي - ليس فقط عند تسجيل الدخول، ولكن طوال الجلسة بأكملها.
على عكس المصادقة القديمة والتقليدية، تم تصميم المصادقة الحديثة لتلبية مستوى النضج الأمثل للثقة الصفرية كما هو محدد من قبل المعهد الوطني للمعايير والتكنولوجيا والابتكار. يجب أن تستوفي المصادقة الحديثة هذه المعايير:
- أمان أقوى بدون كلمات مرور-إزالة الأسرار المشتركة التي يستغلها المهاجمون
- التحقق المستمر من الهوية-الاستفادة من إشارات المخاطر وسياق الجهاز وتحليلات السلوك
- يعمل في كل مكان، للجميع-سواء كانت المصادقة الحديثة في مكان العمل أو السحابة أو المختلطة، يجب أن تؤمن المصادقة الحديثة جميع المستخدمين وجميع الأجهزة وجميع البيئات
1. آمن من طرف إلى طرف:
مقاومة التصيد الاحتيالي ليست كافية. يجب أن يكون حل المصادقة الحديث مقاومًا للبرمجيات الخبيثة، والاحتيال، وهجمات القوة الغاشمة، وتقنيات التجاوز، والانقطاع، وكلها ساهمت في الاختراقات الأخيرة.
الاعتبارات الرئيسية:
- هل تحمي طريقة المصادقة الخاصة بك من اختطاف الجلسة والرموز المميزة للجلسة المسروقة؟
- هل يمكن أن يمنع التفجير الفوري للمصادقة MFA وحشو بيانات الاعتماد؟
- هل هو مرن في حالة انقطاع التيار الكهربائي أم أن مؤسستك ستكون مغلقة؟
2. كلمة مرور من طرف إلى طرف بدون كلمة مرور
لا تزال المصادقة المصفوفة التقليدية تعتمد على كلمات المرور: في معظم الحالات، لا تزال المصادقة المصفوفة التقليدية تعتمد على طريقة تعتمد على كلمة المرور للإعداد أو استعادة بيانات الاعتماد أو مراحل أخرى في دورة حياة الهوية. ويميل المستخدمون إلى إدخال كلمات المرور أولاً لبدء تحدي المصادقة المصادقة المصغرة أولاً، وللتسجيل في المصادقة المصغرة في البداية، ولإعادة تعيين المصادقة المصغرة إذا لزم الأمر. وهذه مشكلة، لأن التهديدات مثل البرمجيات الخبيثة، ورذاذ كلمة المرور، وتفجير المصادقة المصغّرة MFA لا يزال بإمكانها استغلال كلمة المرور الأعمق والجذرية.
يجب أن تعني كلمة المرور الخالية من كلمات المرور ذلك بالضبط. يجب أن يلغي نهج المصادقة الحديث كلمات المرور تمامًا ويجب أن يتضمن:
- جهاز و/أو مفتاح مرور محمول لجميع المستخدمين
- المصادقة الحديثة للخوادم والحواسيب المركزية والبنية التحتية لتكنولوجيا المعلومات
- خيارات متعددة بدون كلمة مرور لتسجيل الدخول إلى سطح المكتب لنظامي التشغيل Windows و macOS
- كلمة مرور احتياطية بدون كلمة مرور لمرة واحدة لكل شيء آخر.
لذا، اسأل نفسك، هل يقوم حل المصادقة الخاص بك بإزالة كلمات المرور بالفعل، أم أنه يضع طبقة أمان فوقها فقط؟
3. تعمل في كل مكان وللجميع
تعمل الشركات عبر البيئات السحابية والهجينة والمحلية. أي استراتيجية مصادقة لا تعتمد على البنية التحتية تخلق ثغرات أمنية.
الأسئلة التي يجب طرحها:
- هل يعمل حل المصادقة الخاص بك عبر جميع الأنظمة الأساسية (ويندوز، ماك أو إس، لينكس، الجوال، الخوادم المحلية)؟ ماذا عن التطبيقات القديمة؟
- هل هو مرن؟ هل يمكنه دعم تجاوز الفشل الهجين والوصول دون اتصال بالإنترنت في السيناريوهات الحرجة؟
- هل يتسع نطاقه ليشمل جميع المستخدمين، بما في ذلك الموظفين والمتعاقدين والمشرفين المميزين؟
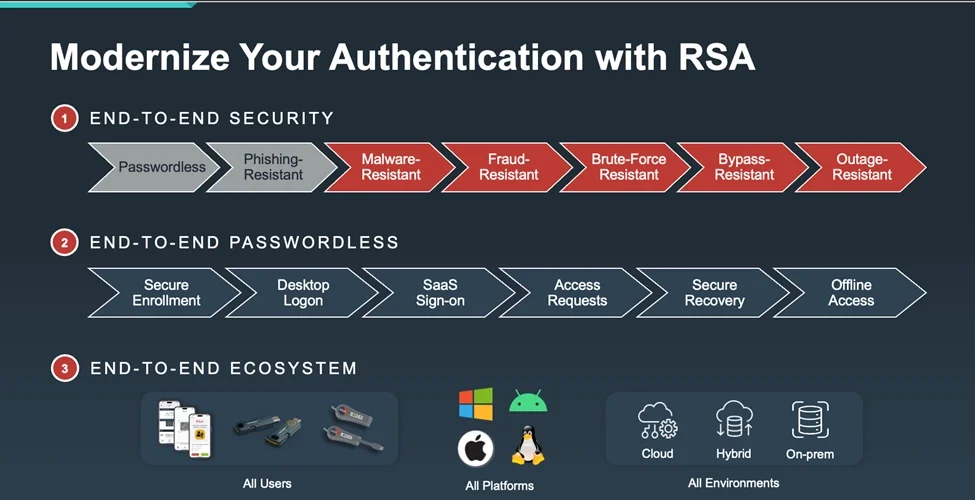
مستقبل المصادقة ليس مجرد مصادقة MFA مقاومة للتصيد الاحتيالي. بدلاً من ذلك، فهو بدون كلمة مرور ومرن وآمن عبر دورة حياة الهوية بأكملها.
تحتاج المؤسسات التي لديها عمليات ذات مهام حرجة إلى حلول تحمي من التهديدات التي تعتمد على الذكاء الاصطناعي والتزييف العميق وتقنيات تجاوز بيانات الاعتماد، وتظل متاحة على الرغم من انقطاع الطرف الثالث، وتحافظ على سياسات المصادقة طوال دورة حياة الهوية بأكملها. باختصار، يحتاجون إلى مصادقة حديثة بدون كلمة مرور.
هل أنت مستعد لإعادة التفكير في استراتيجية المصادقة الخاصة بك؟ حان الوقت لتبني نهج حديث ومتكامل.



